How Long Does TMJ last? Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and More
Temporomandibular joint disorder, or TMJ, is a common and misunderstood condition affecting millions worldwide. If you’re grappling with TMJ, you likely have numerous questions, including, “How long does TMJ last?” This comprehensive guide will explore the intricate world of TMJ, covering everything from its duration and common causes to the symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, prevention strategies, and more. By the end of this article, you will have a clear grasp of the TMJ landscape and be equipped with the knowledge to manage this condition effectively.
Understanding TMJ
What is TMJ?
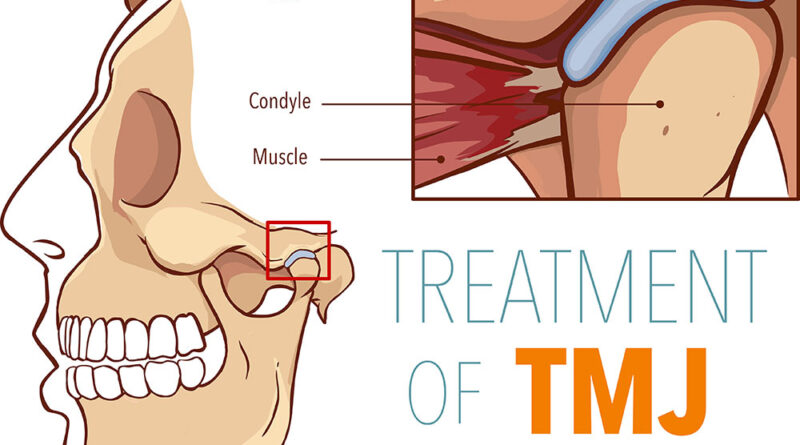
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is a remarkable hinge-like joint that connects your jawbone to your skull, enabling essential functions like chewing, talking, and yawning. When this intricate joint malfunctions, it leads to a condition known as TMJ disorder or TMD. TMJ can be a source of discomfort and distress, and its duration can vary significantly from one person to another.
How Long Does TMJ Last?
The duration of TMJ can be highly variable, contingent upon several factors:
- Severity: The severity of your TMJ condition plays a pivotal role in its duration. Milder cases may resolve more swiftly, while severe cases may persist for an extended period.
- Treatment: The effectiveness of treatment can significantly impact the course of TMJ. Timely intervention and tailored treatment plans can expedite recovery.
- Individual Differences: Each body responds uniquely to TMJ, making it challenging to predict precisely how long the condition will last. Genetics, overall health, and lifestyle choices can influence the duration.
Phases of TMJ Duration
To better understand the potential duration of TMJ, it can be categorized into three phases:
- 1. Acute TMJ: This phase typically lasts a few weeks to a few months. Factors like stress, trauma, or dental issues often trigger acute TMJ. With appropriate self-care and treatment, acute TMJ can resolve relatively quickly.
- 2. Subacute TMJ: Subacute TMJ may persist for several months. During this phase, symptoms can linger despite attempts at self-management. Seeking professional treatment becomes crucial to prevent the condition from becoming chronic.
- 3. Chronic TMJ: TMJ can evolve into a chronic condition if left untreated or if underlying causes are not adequately addressed. Chronic TMJ may persist for years, significantly impacting a person’s quality of life. Effective management and ongoing care are essential to alleviate symptoms and improve daily functioning.
Early intervention and tailored treatment are key to determining how long TMJ will last in your specific case. Seeking the guidance of a healthcare professional experienced in TMJ management is crucial for faster recovery and improved long-term outcomes.
Common Causes of TMJ
Understanding the underlying causes of TMJ can empower you to prevent its onset and manage it more effectively. Here are some common causes and contributing factors:
1. Jaw Injury
Trauma to the jaw, such as a blow or accident, can lead to TMJ. Injuries may result from sports, accidents, or physical altercations, causing damage to the TMJ and surrounding structures.
2. Teeth Grinding (Bruxism)
Excessive clenching or teeth grinding, often due to stress, can strain the TMJ. Bruxism can occur during the day or, more commonly, at night during sleep, making it challenging to control.
3. Arthritis
Various forms of arthritis, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, can affect the TMJ. Inflammation and damage to the joint can lead to TMJ symptoms, particularly in older individuals.
4. Dental Problems
Issues with your dental alignment or dental work can contribute to TMJ. Malocclusion, or a misaligned bite, can place undue stress on the joint, as can missing teeth or poorly executed dental procedures.
5. Stress
High-stress levels can manifest as jaw tension, leading to the worsening of TMJ symptoms. Stress management techniques can be invaluable in reducing TMJ-related discomfort.
6. Genetics
In some cases, genetics may play a role in predisposing individuals to TMJ. If family members have experienced TMJ, you may be more likely to develop the condition.
7. Poor Posture
Incorrect posture, especially regarding neck and head positioning, can contribute to TMJ symptoms. Maintaining good posture can help alleviate some of the strain on the TMJ.
Understanding these causes can help you identify potential risk factors and take steps to mitigate them.
Symptoms of TMJ
TMJ is a multifaceted condition that can manifest through various symptoms, which can vary in intensity. Common TMJ symptoms include:
Pain
Pain is a hallmark symptom of TMJ and can manifest in various areas, including the jaw, face, and ear. This pain can be intermittent or constant and may worsen with jaw movement.
Limited Jaw Movement
Opening or closing the mouth entirely is a common issue for those with TMJ. This limitation in jaw movement can impact daily activities like eating and speaking.
Clicking or Popping Sounds
Some individuals may hear clicking, popping, or grinding sounds when they move their jaw. These sounds can be disconcerting and are often accompanied by discomfort.
Headaches
TMJ-related tension can lead to frequent headaches, often resembling migraines. These headaches can radiate from the jaw area to other head parts.
Earaches
Pain in the ears can be a result of TMJ dysfunction. This discomfort may be mistaken for an ear infection or other ear-related conditions.
Neck and Shoulder Pain
TMJ can also cause discomfort in the neck and shoulders due to muscle tension. The interconnectedness of these muscles and the jaw can lead to referred pain.
Tinnitus
Some individuals with TMJ may experience ringing or buzzing in the ears, known as tinnitus. This symptom can be exceptionally bothersome and impact daily life.
Dizziness
In rare cases, TMJ can cause dizziness and vertigo. These symptoms may occur due to the proximity of the inner ear structures to the TMJ.
Understanding these symptoms is essential for early recognition and prompt treatment of TMJ. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s necessary to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
Diagnosing TMJ
Accurate diagnosis is a crucial first step in effectively managing TMJ. When you present with TMJ symptoms, your healthcare provider will perform a comprehensive evaluation, which may include:
- Medical History: Your healthcare provider will ask about your medical history, including any previous jaw injuries, dental work, or family history of TMJ.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination will assess your jaw’s range of motion, muscle tenderness, and any unusual sounds during jaw movement.
- Imaging: In some cases, imaging studies such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs may be necessary to visualize the TMJ and surrounding structures.
- Dental Examination: Your dentist may examine your bite, dental alignment, and tooth condition to rule out dental causes of TMJ symptoms.
- Additional Tests: Additional tests or consultations with specialists may be recommended depending on your specific symptoms and medical history.
Once a diagnosis is established, you and your healthcare provider can discuss appropriate treatment options tailored to your needs.
Treatment Options
The management of TMJ is multifaceted and often involves a combination of approaches. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of your condition and may include:
Self-Care Techniques
- Rest: Give your jaw a break by avoiding hard, chewy, or tough-to-eat foods. Stick to a soft diet if necessary.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold packs to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Jaw Exercises: Gentle jaw exercises prescribed by a healthcare professional can improve mobility and reduce discomfort.
- Stress Management: Practicing relaxation techniques can alleviate jaw tension caused by stress.
Medications
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or prescription medications can help manage pain and inflammation.
- Muscle Relaxants: These medications may be prescribed to reduce muscle tension in the jaw.
- Anti-Anxiety Medications: In cases where stress and anxiety contribute to TMJ, anti-anxiety medications may be beneficial.
Dental Treatments
- Orthodontic Work: Correcting dental misalignments through orthodontic treatments can alleviate TMJ symptoms.
- Dental Splints or Night Guards: These oral appliances help prevent teeth grinding and jaw clenching.
Physical Therapy
A physical therapist can provide exercises and techniques to improve jaw mobility, strengthen muscles, and reduce pain.
Injections
In some cases, corticosteroid injections directly into the TMJ can relieve pain and inflammation.
Surgery
Surgery is typically considered when conservative treatments are ineffective or in severe cases. Surgical options may include arthrocentesis, arthroscopy, or open-joint surgery.
Discussions with your healthcare provider will determine the treatment choice, considering your specific symptoms and their severity.
TMJ Exercises
Exercise can play a pivotal role in managing TMJ. Here are some simple activities you can try:
1. Jaw Stretching
- Gently open your mouth as wide as comfortable.
- Hold for 5-10 seconds.
- Close your mouth slowly.
- Repeat this exercise 5-10 times, gradually increasing repetitions.
2. Resisted Jaw Opening
- Place your thumb under your chin.
- Try to open your mouth while applying gentle resistance with your thumb.
- Hold for 3-5 seconds.
- Release and repeat 5-10 times.
3. Chin Tucks
- Sit or stand up straight.
- Slowly and gently tuck your chin toward your chest.
- Hold for 3-5 seconds.
- Repeat 5-10 times.
4. Tongue-Up
- Press your tongue against the roof of your mouth.
- Hold for 3-5 seconds.
- Repeat 5-10 times.
These exercises can help improve jaw mobility and reduce tension. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist before starting any exercise regimen to ensure they are appropriate for your condition.
Preventing TMJ
While not all cases of TMJ can be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk and minimize symptoms:
1. Stress Management
Stress reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce jaw tension.
2. Avoid Teeth Grinding
If you grind your teeth, consider wearing a night guard or dental splint to protect your teeth and jaw during sleep.
3. Maintain Good Posture
Be mindful of your posture, especially regarding your head and neck position. Proper ergonomics can alleviate strain on the jaw.
4. Avoid Chewing Gum and Tough Foods
Chewing gum and consuming tough or chewy foods can strain the jaw. Opt for a softer diet if you are experiencing TMJ symptoms.
5. Stay Hydrated
Dehydration can exacerbate muscle tension. Ensure you drink enough water throughout the day.
FAQs About TMJ
Q1: Is TMJ a common condition?
A: TMJ is relatively joint, with millions of individuals experiencing its symptoms. It can affect people of all ages, although it is more prevalent among adults.
Q2: Are there home remedies for TMJ relief?
A: Yes, several home remedies can provide relief from TMJ symptoms, including heat or cold therapy, jaw exercises, and stress management techniques.
Q3: Can TMJ go away on its own without treatment?
A: In some cases, TMJ symptoms may improve or resolve independently, mainly if temporary factors like stress trigger them. However, seeking treatment is often recommended for a faster recovery and better outcomes.
Q4: Is surgery the only option for severe TMJ cases?
A: No, surgery is typically considered when conservative treatments are ineffective or in severe cases. Most individuals with TMJ find relief through less invasive treatments, such as medication, physical therapy, or dental interventions.
Q5: Can TMJ be related to dental problems?
A: Dental problems like misaligned teeth or a poor bite (malocclusion) can contribute to TMJ symptoms. Addressing these dental issues can help alleviate TMJ discomfort.
Q6: How can I find a healthcare provider experienced in TMJ treatment?
A: You can start by consulting your primary care physician or dentist, who can provide referrals to specialists, such as oral and maxillofacial surgeons or TMJ specialists.
Q7: Are there any foods I should avoid if I have TMJ?
A: It’s advisable to avoid hard, chewy, or tough-to-eat foods if you have TMJ, as they can exacerbate symptoms. Opt for a softer diet that places less strain on the jaw.
Q8: Can stress worsen TMJ symptoms?
A: Stress can exacerbate TMJ symptoms by causing increased jaw tension and teeth grinding. Stress management techniques can be beneficial in reducing TMJ-related discomfort.
Conclusion
In conclusion, TMJ is a multifaceted condition with variable duration and potential causes. Understanding the intricacies of TMJ, from its common causes to its symptoms and treatment options, is crucial for effective management. If you are experiencing TMJ symptoms, seeking timely medical evaluation and treatment is essential to improve your quality of life and prevent the condition from becoming chronic. By implementing preventive measures and exploring appropriate remedies, you can take control of your TMJ and work towards a healthier, pain-free future.