Unveiling the Mystery of Mango Worms: Symptoms, prevention, treatment
Have you ever heard of mango worms? These tiny creatures might not be the most popular topic of conversation, but they are certainly intriguing and worth exploring. Let’s take a look into the fascinating world of mango worms, from their life cycle to treatment options and everything in between. So, sit back, relax, and let’s uncover the secrets of these peculiar parasites.
What Are Mango Worms?
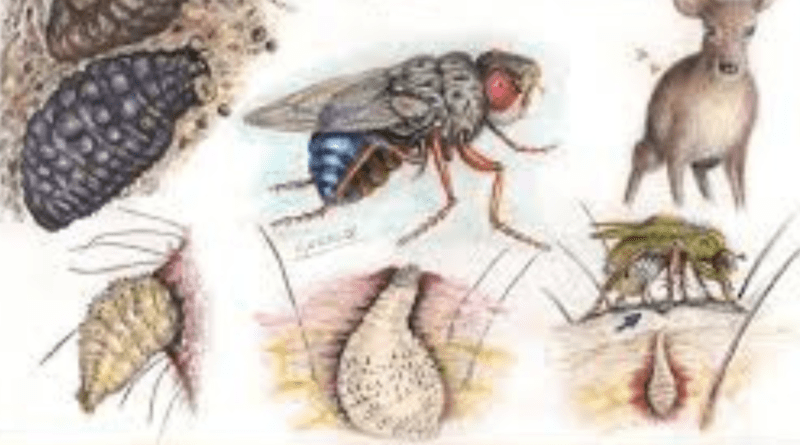
Mango worms, scientifically known as Cordylobia anthropophagy, are a type of skin-dwelling parasitic fly larvae that predominantly affect mammals, including humans. These small, yellowish-white larvae are commonly found in sub-Saharan Africa, particularly in rural areas. Their name derives from the misconception that mango flies, a different species, are responsible for their transmission. In reality, mango worms are the larvae of the tumbu fly.
Life Cycle of Mango Worms
Understanding the life cycle of mango worms is essential to combat these tiny intruders effectively. The process begins when an adult female tumbu fly lays her eggs on damp clothing or in the sand.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
Egg Deposition: The female fly deposits her eggs in a location where potential hosts, such as mammals, might come into contact with them.
Penetration: When a mammal brushes against the eggs, the warmth of the host’s body triggers the eggs to hatch, releasing tiny larvae.
Infection: The larvae penetrate the host’s skin, usually through hair follicles or small cuts, within minutes of hatching.
Feeding: Once inside the host’s body, the larvae create small, painful bumps while they feed on tissue fluids.
Pupation: After about a week, the fully grown larvae exit the host’s skin, drop to the ground, and pupate in the soil.
Emergence: Adult tumbu flies emerge from pupation, and the cycle repeats.
The Impact of Mango Worms
Mango worms might be small, but their impact can be significant. They can cause a range of health issues and discomfort for their hosts. Common symptoms include:
Itching: The presence of mango worms under the skin can lead to intense itching, making it difficult for affected individuals to focus on their daily tasks.
Infection: Scratching the affected area can introduce bacteria, leading to skin infections.
Pain: The feeding activity of mango worm larvae can cause pain, making it essential to address the issue promptly.
Secondary Complications: In severe cases, mango worm infestations can lead to more severe complications, such as cellulitis or abscess formation.
Treatment Options for Mango Worms
If you find yourself dealing with mango worms, it’s essential to know how to treat them effectively. While there are medical treatments available, some home remedies can also help alleviate the discomfort.
How to managing mango worm infestations:
Identify the Infection: The first step is to confirm the presence of mango worms. Look for small, raised bumps on the skin that might have a tiny hole at the center.
Sterilize the Area: Clean the affected area with an antiseptic solution to reduce the risk of infection.
Extraction: Gently, but firmly, apply pressure around the mango worm bump. This can encourage the worm to emerge from the hole. Avoid squeezing too hard, as it can cause the worm to rupture, potentially leading to infection.
Use Tweezers: If the worm doesn’t emerge on its own, carefully use tweezers to grasp it at the surface and slowly pull it out. Ensure the tweezers are sterilized.
Clean and Disinfect: After extraction, clean the wound thoroughly and apply an antiseptic ointment to prevent infection.
Monitor for Infection: Keep an eye on the area for any signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or pus. If infection occurs, seek medical attention promptly.
It’s crucial to note that while home treatment can be effective, severe infestations or complications may require professional medical intervention.
Prevention is Key
As the saying goes, prevention is better than cure. To reduce the risk of mango worm infestations, consider the following preventive measures:
Protective Clothing: When in areas where mango worms are prevalent, wear long sleeves and trousers to minimize skin exposure.
Insect Repellent: Apply insect repellent to exposed skin to deter tumbu flies.
Regular Hygiene: Maintain good personal hygiene practices, such as bathing regularly and keeping your clothing clean.
Inspect Bedding: Check bedding and clothing for any signs of eggs or larvae before use.
Environmental Control: Keep your living area clean and free from damp, as tumbu flies tend to lay their eggs in such conditions.
Conclusion
Mango worms may be tiny, but their impact on those they infest can be significant. Understanding their life cycle, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for anyone living in or traveling to regions where these parasites are prevalent. By following proper prevention measures and having the right products on hand, you can enjoy peace of mind and confidently protect yourself and your loved ones from these intriguing but unwelcome guests.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are mango worms, and how do they affect humans?
Mango worms, scientifically known as Cordylobia anthropophagy, are the larvae of tumbu flies. These small, yellowish-white larvae burrow into the skin of mammals, including humans, where they feed on tissue fluids. Their presence can cause itching, pain, and even infection if not properly treated.
2. Where are mango worms commonly found?
Mango worms are primarily found in sub-Saharan Africa, particularly in rural areas with warm and humid climates. They are known to thrive in sandy soil and damp conditions, making rural regions with limited sanitation more susceptible to infestations.
3. How can I prevent mango worm infestations when traveling to affected areas?
To reduce the risk of mango worm infestations while traveling to affected areas, consider the following preventive measures:
Wear protective clothing, such as long sleeves and trousers, to minimize skin exposure.
Apply insect repellent to exposed skin to deter tumbu flies.
Maintain good personal hygiene practices, including regular bathing and clean clothing.
Inspect bedding and clothing for any signs of eggs or larvae before use.
Keep your living area clean and free from damp conditions, as tumbu flies lay their eggs in such environments.
4. What should I do if I suspect a mango worm infestation?
If you suspect a mango worm infestation, follow these steps:
Identify the infected area, typically marked by small raised bumps on the skin with a tiny hole at the center.
Clean the affected area with an antiseptic solution to reduce the risk of infection.
Attempt to extract the worm by gently applying pressure around the bump or using sterilized tweezers to grasp and slowly pull it out.
Clean the wound thoroughly and apply an antiseptic ointment to prevent infection.
Monitor the area for any signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or pus. Seek medical attention if infection occurs or if you’re unable to extract the worm safely.
5. Are there any products available to prevent mango worm infestations?
Yes, there are products designed to help prevent mango worm infestations. These products typically include insect repellents, clothing treated with insect-repellent coatings, and skin protection solutions. It’s advisable to explore reliable mango worm prevention products to ensure you have the right tools to protect yourself when traveling to affected areas.
Remember that while prevention is essential, being informed about mango worms and knowing how to address potential infestations is equally important for your well-being.