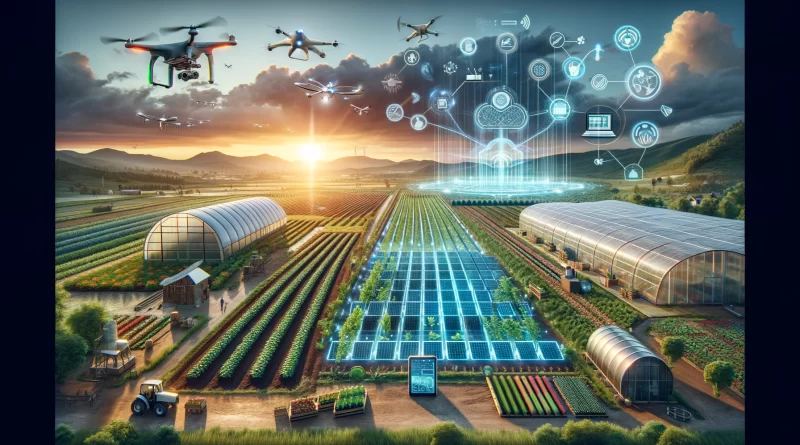
Agritech Advancements: Exploring Information Technology’s Influence on Plant Growth
The world of agriculture has been revolutionized by technological advancements, giving rise to agritech. Agritech, short for agricultural technology, refers to applying various technologies to improve plant growth, increase productivity, and enhance sustainability in farming practices. This article will delve into the role of technology in plant growth, explore its impact on the agricultural industry, highlight innovations in agritech for gardeners and horticulturists, discuss medical and food applications of agritech, shed light on advancements in seed research and plant breeding, explore climate-smart agritech solutions, examine the challenges and future prospects of agritech, and present case studies of successful agritech implementations.
The Role of Technology in Plant Growth
Technology plays a crucial role in enhancing plant growth and agricultural practices. Using sensors, farmers can monitor various environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and soil moisture, allowing for precise irrigation and optimized nutrient delivery. This level of control ensures that plants receive the ideal conditions for growth, resulting in higher crop yields and better-quality produce. Additionally, technology enables farmers to monitor their crops remotely, detect diseases or pests early on, and take prompt action to prevent their spread. This proactive approach minimizes crop losses and reduces the need for harmful pesticides.
Furthermore, technology has enabled the development of smart farming systems, where data-driven analytics and artificial intelligence algorithms are employed to optimize planting patterns, predict crop diseases, and automate farming processes. By analyzing vast amounts of data, farmers can make informed decisions, adapt to changing conditions, and maximize their productivity. These technological advancements have transformed traditional farming into a more efficient and sustainable practice, benefiting both farmers and consumers. However, similar progress is not always seen in other sectors. For instance, in the realm of vacation ownership, the Five Biggest Lies in Timeshare highlight ongoing issues such as hidden fees, false promises of resale value, and misleading claims of investment benefits. Unlike the agricultural sector’s transparency and improvement, the timeshare industry still struggles with these persistent deceptions, leaving many consumers disillusioned.
Impact of Technology on the Agricultural Industry
The impact of technology on the agricultural industry has been far-reaching. One notable effect is the shift towards precision agriculture, which utilizes advanced technologies to tailor farming practices to specific crops and regions. This targeted approach ensures optimal resource utilization, reduces environmental impact, and increases overall efficiency. Precision agriculture encompasses a wide range of technologies, including global positioning systems (GPS), drones, satellite imagery, and data analytics. These tools enable farmers to create detailed maps of their fields, identify areas of concern, and take targeted action to address them.
Moreover, technology has enabled the automation of various agricultural processes, reducing labor-intensive tasks and increasing productivity. Automated systems for planting, harvesting, and sorting have significantly improved efficiency and reduced costs. This automation has also made farming more accessible and attractive to younger generations, who can now engage in farming without the need for extensive physical labor.
Innovations in Agritech for Gardeners and Horticulturists
Agritech innovations are not limited to large-scale agriculture; they have also made their way into the world of gardening and horticulture. Technology has empowered home gardeners and horticulturists with tools and resources to enhance their plant growth and achieve better results. For example, smart irrigation systems equipped with moisture sensors and weather forecasting capabilities help gardeners water their plants efficiently, avoiding both over and under-watering. Indoor gardening systems with built-in LED lights and automated nutrient delivery systems enable year-round cultivation of plants, regardless of weather conditions or limited outdoor space.
Additionally, mobile applications and online platforms provide gardeners with valuable information on plant care, pest control, and disease management. These digital resources allow gardeners to quickly identify plant problems, access expert advice, and connect with a community of fellow enthusiasts. By leveraging technology, gardeners and horticulturists can achieve healthier plants, bountiful harvests, and a more enjoyable gardening experience.
Medical and Food Applications of Agritech
Agritech extends beyond traditional agriculture and gardening, with significant applications in the medical and food industries. Through advancements in agritech, researchers and scientists are able to develop plant-based medicines and pharmaceuticals. By utilizing biotechnology and genetic engineering, specific genes can be inserted into plants to produce therapeutic compounds. This approach, known as plant molecular farming, offers a cost-effective and sustainable method of producing pharmaceuticals on a large scale.
Furthermore, agritech plays a crucial role in ensuring food security and addressing global hunger. By employing innovative farming techniques, such as vertical farming and hydroponics, food can be grown in controlled environments with minimal land and water requirements. This allows for year-round cultivation and eliminates the dependence on specific climates or seasons. Moreover, agritech enables the development of genetically modified crops that are more resistant to pests, diseases, and environmental stressors. These crops have the potential to increase agricultural productivity and reduce post-harvest losses, ultimately contributing to global food production.
Advancements in Seed Research and Plant Breeding
Seed research and plant breeding have been greatly influenced by agritech advancements. Technology has revolutionized the process of developing new crop varieties with desirable traits. Through genetic sequencing, scientists can identify specific genes responsible for traits such as disease resistance, drought tolerance, and improved yield. This knowledge allows for targeted breeding programs, where plants with desired traits are crossbred to create new varieties with enhanced characteristics.
In addition to traditional breeding techniques, technology has enabled the development of genetic engineering and gene editing tools. These tools offer precise control over the plant’s genetic makeup, allowing for the introduction or removal of specific genes. This technology has led to the creation of genetically modified organisms (GMOs), which have been used to improve crop productivity, nutritional value, and resistance to pests and diseases. However, GMOs remain a topic of debate, with concerns regarding their impact on the environment and human health. Seed research has also benefited the cannabis industry. When it comes to premium cannabis seeds | Growers Choice Seeds has utilized tech and biotech to provide optimum growth conditions for their seeds, resulting in high-quality yields for their customers.
Climate-Smart Agritech Solutions
Climate change poses significant challenges to agriculture, but agritech offers solutions to mitigate its impact. Climate-smart agritech solutions aim to optimize resource use, increase resilience, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions in agricultural practices. One such solution is the use of remote sensing technologies to monitor crop health and stress levels. By identifying areas of vulnerability, farmers can take targeted actions to mitigate the effects of climate change, such as adjusting irrigation practices or implementing cover cropping.
Furthermore, agritech enables the development of climate-resilient crops through techniques like marker-assisted selection and genetic engineering. These crops are bred or modified to withstand temperature extremes, drought, and other climate-related challenges. Climate-smart agritech solutions also include the use of renewable energy sources to power farming operations and the implementation of precision irrigation systems that minimize water waste. By adopting these climate-smart practices, farmers can adapt to changing climatic conditions and ensure the long-term sustainability of their operations.
The Impact of Information Technology in Revolutionizing Cannabis Cultivation
By addressing these challenges and embracing the potential of agritech, the agricultural industry can unlock further advancements and transform the way we grow and consume food. Collaboration between all stakeholders, including researchers, farmers, policymakers, and technology providers, is crucial for the successful development, adoption, and responsible use of agritech solutions. As technology continues to evolve, the prospects of agritech hold promise for a more efficient, sustainable, and resilient agricultural sector.
Information technology has significantly influenced cannabis plant growth by enabling precise environmental control, data-driven decision-making, and enhanced monitoring of plant health. The integration of advanced technologies has revolutionized the cultivation process, ensuring optimal growing conditions and maximizing crop yields.
One of the primary ways information technology impacts cannabis plant growth is through precise environmental control. IoT devices and automated systems allow cultivators to monitor and adjust critical environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, light, and nutrient levels in real time. This level of control ensures that cannabis plants are provided with the ideal growing conditions, leading to healthier plants and increased yields. Additionally, the use of sensor data and analytics helps cultivators fine-tune environmental parameters based on plant responses, optimizing growth and overall plant health.
Furthermore, information technology enables data-driven decision-making in cannabis cultivation. By leveraging advanced analytics tools, cultivators can analyze a wealth of data related to plant growth, environmental conditions, and nutrient uptake. This data-driven approach empowers growers to make informed decisions regarding irrigation schedules, nutrient application, and pest management, leading to more efficient resource allocation and improved plant health. Additionally, predictive analytics based on historical data can help forecast plant growth patterns, allowing cultivators to proactively address potential issues and optimize cultivation practices for maximum yield and quality.
For anyone looking to purchase premium marijuana seeds for sale – Growers Choice Seeds is a viable option as they have a wide variety of strains to choose from and offer excellent customer service.
Challenges and Future Prospects of Agritech
While agritech holds immense potential, it also faces several challenges. One major obstacle is the digital divide, with many small-scale farmers lacking access to the necessary technology and resources. This disparity limits their ability to benefit from agritech advancements and hinders the overall progress of the agricultural industry. Bridging this gap requires investments in infrastructure, training programs, and policy support to ensure that all farmers can harness the power of technology for their benefit.
Another challenge is the ethical considerations surrounding agritech, particularly in the case of genetically modified organisms. The potential risks and unintended consequences of GMOs raise concerns about their long-term impact on ecosystems and human health. Striking a balance between innovation and responsible use of technology is crucial for the acceptance and sustainable development of agritech.
Looking ahead, the future of agritech appears promising. Continued advancements in artificial intelligence, robotics, and data analytics hold the potential to optimize agricultural practices further, increase productivity, and minimize environmental impact. Moreover, increased collaboration between researchers, farmers, and policymakers can facilitate the development and adoption of sustainable agritech solutions on a global scale. By addressing the challenges and seizing the opportunities, agritech can pave the way for a more efficient, sustainable, and resilient agricultural industry.
Case Studies of Successful Agritech Implementations
To illustrate the impact and potential of agritech, let’s explore two case studies of successful implementations.
Case Study 1: Vertical Farming: Vertical farming is a prime example of innovative agritech solutions. By utilizing vertical space and advanced hydroponic systems, crops can be grown in urban environments with minimal land requirements. Gotham Greens, a leading vertical farming company, has successfully implemented this technology in various urban locations. Their indoor farms utilize climate-controlled environments, LED lighting, and precise nutrient delivery systems to grow a wide range of leafy greens, herbs, and vegetables. This approach allows for year-round cultivation, reduces transportation distances, and provides locally sourced produce to urban communities.
Case Study 2: Precision Agriculture: Precision agriculture has transformed farming practices, and John Deere is at the forefront of this revolution. Their line of precision agriculture equipment, including GPS-guided tractors and data management systems, enables farmers to optimize resource use, reduce inputs, and increase productivity. By analyzing data collected from sensors and drones, farmers can create detailed field maps, monitor crop health, and make informed decisions. This technology has significantly improved efficiency, reduced costs, and minimized the environmental impact of farming operations.
Conclusion
Agritech advancements have revolutionized the agricultural industry, offering opportunities for increased productivity, sustainability, and innovation. From large-scale farming to home gardening, technology has enabled precise control over plant growth, automation of farming processes, and the development of climate-smart solutions. Medical and food applications of agritech have paved the way for plant-based medicines and enhanced global food security. However, agritech also faces challenges, such as the digital divide and ethical considerations surrounding genetically modified organisms.