How Long Can You Keep Your Teeth With Periodontal Disease? Understanding Your Dental Health
Periodontal Disease, commonly known as gum disease, is a widespread and serious oral health condition that affects millions globally. This condition, which can progress from mild gum inflammation to severe tissue damage and tooth loss, poses a major risk to overall dental health. This comprehensive guide will cover essential information about the stages of periodontal disease, available treatments, and how to maintain your teeth for as long as possible. Just as preventive measures are vital in health, staying informed about Which Games are Hot in 2024? can be essential for those in the gaming community. In 2024, top trending games span diverse genres—from immersive RPGs and strategic simulators to fast-paced battle royales, catering to a variety of gaming preferences and helping players stay engaged and entertained.
Understanding Periodontal Disease
Before delving into how long you can retain your teeth with periodontal Disease, it’s essential to understand the Disease itself.
Periodontal Disease Defined: Periodontal Disease is a chronic bacterial infection primarily affecting the gums and the bone supporting your teeth. It typically begins as gingivitis, which is characterized by inflammation of the gums and may progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of the Disease.
The Role of Plaque: The primary culprit behind periodontal Disease is dental plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth. If not adequately removed through proper oral hygiene practices like brushing and flossing, plaque can harden into tartar, leading to gum irritation and inflammation.
The Stages of Periodontal Disease
Periodontal Disease progresses through distinct stages, each with its characteristics and implications for dental health.
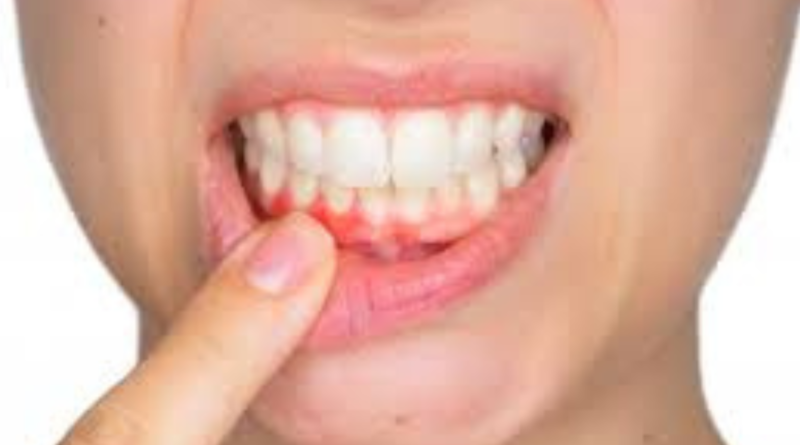
- Gingivitis: Gingivitis marks the early stage of periodontal Disease. Symptoms include red, swollen gums that may bleed during brushing or flossing. The damage at this stage is usually reversible with appropriate dental care, emphasizing regular cleanings and improved oral hygiene habits.
- Periodontitis: If gingivitis goes untreated, it can advance to periodontitis. This stage involves the loss of bone and gum tissue supporting your teeth. Gum pockets may form, allowing harmful bacteria to thrive causing further damage. As periodontitis progresses, teeth may become loose and even lead to tooth loss.
Factors Influencing Tooth Preservation
Several factors come into play when determining how long you can keep your teeth with periodontal Disease:
- Early Detection: Timely diagnosis and intervention play a crucial role in preserving teeth. Seeking professional dental care at the earliest signs of gum disease can prevent irreversible damage.
- Severity of Disease: The extent of gum and bone loss due to periodontal Disease affects the prognosis. Less severe cases are more manageable, while advanced topics may require more intensive treatment.
- Treatment and Management: Effective management of periodontal disease involves scaling and root planning (deep cleaning) to remove plaque and tartar. Surgical interventions may be necessary in severe cases. Maintenance through regular dental visits and proper oral hygiene habits is essential for long-term tooth preservation.
Preserving Your Teeth with Periodontal Disease
Now that we’ve covered the critical aspects, let’s explore how you can maximize the chances of retaining your teeth when dealing with periodontal Disease:
1. Early Intervention
Early detection is critical to successful treatment. Consult your dentist promptly if you notice symptoms like bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, or gum recession.
2. Professional Treatment
Dental professionals can assess the extent of your periodontal Disease and recommend appropriate treatments. This may include scaling and root planing, laser therapy, or, in advanced cases, surgical procedures.
3. Improved Oral Hygiene
Commit to an enhanced oral hygiene routine. Brush your teeth at least twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, floss daily, and use an antiseptic mouthwash. Your dentist or periodontist can guide you through the best practices for your specific condition.
4. Regular Dental Visits
Consistent dental check-ups and cleanings are vital. These visits allow your dental care team to monitor the progress of your periodontal Disease, make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan, and catch potential issues early.
The Longevity of Teeth With Periodontal Disease
Now, let’s address the central question: how long can you expect to keep your teeth with periodontal Disease? The answer largely depends on your commitment to treatment and management.
In the early stages, such as gingivitis, prompt intervention and improved oral hygiene can reverse gum inflammation and prevent further damage. With effective treatment and diligent care, many individuals with periodontal Disease maintain their natural teeth for years, if not a lifetime.
For those facing more advanced cases of periodontitis, the outcome may involve a combination of treatments, including surgical procedures. While tooth loss remains a possibility, these interventions can significantly extend the longevity of your teeth.
Conclusion: Your Role in Tooth Preservation
In conclusion, the length of time you can keep your teeth with periodontal Disease is not solely determined by the Disease itself. Your proactive approach to treatment, oral hygiene, and regular dental care is pivotal in preserving your teeth.
Periodontal Disease, though challenging, is manageable and treatable. Don’t delay seeking professional dental care if you suspect gum disease. With the right interventions and your commitment to maintaining good oral health practices, you can enjoy a future with a healthy and functional set of teeth, even in the face of periodontal Disease.
Individual experiences may vary, and treatment success depends on various factors. Consult your dentist or periodontist for personalized guidance on managing periodontal Disease and preserving dental health.